Журнал «Почки» Том 13, №4, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Ефективність наповнювачів у боротьбі зі стресовим і змішаним нетриманням сечі: систематичний огляд та метааналіз
Авторы: Alma Dhiani Paramita (1), Fiqih Faizara Ustadi (1), Jennifer Susanto (1), Moch. Afrizal Ansori (1), Eighty Mardiyan Kurniawati (2), Tri Hastono Setyo Hadi (2)
(1) - Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Indonesia
(2) - RSUD Dr. Soetomo, Indonesia
Рубрики: Нефрология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
Стресове нетримання сечі й змішане нетримання сечі з переважанням стресового компонента є поширеними станами, що значно погіршують якість життя, особливо серед жінок. Уретральні наповнювачі з’явилися як варіант нехірургічного лікування пацієнтів, які вагаються щодо оперативного втручання. Метою цього систематичного огляду та метааналізу є оцінка ефективності й безпеки різних наповнювачів уретри, зокрема Bulkamid, Macroplastique і Urolastic, у лікуванні стресового нетримання сечі та змішаного нетримання сечі з переважанням стресового компонента. Огляд охоплює 15 досліджень, включно з рандомізованими контрольованими й когортними дослідженнями, із загальною кількістю 1120 пацієнтів. Автори зосереджуються на показниках одужання й покращення стану пацієнтів, ускладненнях і ризику системної помилки. За результатами дослідження, показники одужання й покращення коливаються в діапазоні від 70 до 80 %, із зведеним середнім 75 %. Аналіз по підгрупах виявив, що показники одужання становили 76 % для Bulkamid, 73 % для Urolastic і 77 % для Macroplastique. Незважаючи на значну статистичну неоднорідність, зокрема для Bulkamid та Urolastic, результати свідчать про те, що ці засоби можуть бути ефективними нехірургічними варіантами. Проте в огляді підкреслюється необхідність проведення добре спланованих рандомізованих контрольованих досліджень для подальшої оцінки довгострокової ефективності й безпеки цих методів з метою оптимізації результатів лікування пацієнтів.
Stress urinary incontinence and stress-predominant mixed urinary incontinence are prevalent conditions that significantly impair quality of life, particularly among women. Urethral bulking agents have emerged as a non-surgical treatment option for patients who are hesitant to undergo surgical interventions. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of various urethral bulking agents, specifically Bulkamid, Macroplastique, and Urolastic, in treating stress urinary incontinence and stress-predominant mixed urinary incontinence. The review encompasses 15 studies, including randomized controlled trials and cohort studies, with a total of 1,120 patients. The analysis focuses on cure and improvement rates, complications, and the risk of bias associated with the included studies. The findings indicate that bulking agents demonstrate cure and improvement rates ranging from 70 to 80 %, with a pooled average of 75 %. Subgroup analyses reveal cure rates of 76 % for Bulkamid, 73 % for Urolastic, and 77 % for Macroplastique. Despite significant statistical heterogeneity, particularly for Bulkamid and Urolastic, the results suggest that these agents can serve as effective non-surgical options. The outcomes appear consistent across all continents included in this study, reinforcing their potential as reliable alternative globally. However, the review highlights the necessity for well-designed randomized controlled trials to further assess the long-term efficacy and safety of these treatments, ultimately aiming to optimize patient outcomes.
стресове нетримання сечі; змішане нетримання сечі; наповнювачі уретри; ефективність; безпека; курси лікування
stress urinary incontinence; mixed urinary incontinence; urethral bulking agents; efficacy; safety; cure rates
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Nitti VW. The prevalence of urinary incontinence. Rev Urol. 2001;3 (Suppl 1):S2-6.
- Viereck V, Bader W, Lobodasch K, Pauli F, Bentler R, Kölbl H. Guideline-Based Strategies in the Surgical Treatment of Female Urinary Incontinence: The New Gold Standard is Almost the Same as the Old One. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2016 Aug;76(8):865-8.
- Corrado B, Giardulli B, Polito F, Aprea S, Lanzano M, Dodaro C. The Impact of Urinary Incontinence on Quality of Life: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Metropolitan City of Naples. Geriatrics. 2020 Nov;5(4):96.(AUGS) AUS. Coding for Urethral Bulking. 2018. Available from: https://www.augs.org/assets/1/6/Coding_Fact_Sheet_for_Urethral_Bulking_2018.pdf.
- Sikora M, Gamper M, Zivanovic I, Münst J, Bischofberger H, Kociszewski J, et al. Current Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence by Bulking Agents and Laser Therapy — An Update. J Clin Med. 2024 Feb;13(5):1377.
- Lemperle G, Lemperle S. Injectable Bulking Agents for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence. SM Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2017;1(1):1-9. Available from: https://www.jsmcentral.org/sm-ge–rontology/fulltext_smggr-v1-1005.pdf.
- Serati M, Mancini V, Balzarro M. Urethral bulking agents for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J. 2020 Aug 3;31(8):1493-4. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00192-019-04221-3.
- Ghoniem G, Farhan B, Chowdhury ML, Chen Y. Safety and efficacy of polydimethylsiloxane (Macroplastique®) in women with stress urinary incontinence: analysis of data from patients who completed three years follow-up. Int Urogynecol J. 2021 Oct;32(10):2835-40.
- Lemmon B, Cardozo L, Bray R, Cortes E. Retrospective ana–lysis of the efficacy and safety of polyacrylamide hydrogel (Bulkamid®) peri-urethral bulking injection at the time of pelvic floor repair in wo–men with pelvic organ prolapse and urodynamic stress incontinence. A pilot study. Continence. 2024 Jun;10:101221. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2772973724001541.
- Hoe V, Haller B, Yao HH, O’Connell HE. Urethral bulking agents for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women: A systematic review. Neurourol Urodyn. 2021 Aug;40(6):1349-88.
- Brosche T, Kuhn A, Lobodasch K, Sokol ER. Seven-year efficacy and safety outcomes of Bulkamid for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2021 Jan 7;40(1):502-8. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/nau.24589.
- Tan X, Li G, Li C, Kong C, Li H, Wu S. Animal models, treatment options, and biomaterials for female stress urinary incontinence. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12.
- Fleischmann NM, Chughtai BM, Plair AM, Hurtado EM, Jacobson NM, Segal SM, et al. Urethral Bulking. Urogynecology. 2024;30(8):667-82.
- Sebesta EM, Dmochowski RR. Mixed Urinary Incontinence: Diagnosis and Management. OBM Geriatr. 2023 Oct 5;7(4):1-22. Available from: https://www.lidsen.com/journals/geriatrics/geriatrics-07-04-251.
- Saraluck A, Chinthakanan O, Kijmanawat A, Aimjirakul K, Wattanayingcharoenchai R, Manonai J. Autologous platelet rich plasma (A-PRP) combined with pelvic floor muscle training for the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence (SUI): A randomized control clinical trial. Neurourol Urodyn. 2024 Feb 18;43(2):342-53. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/nau.25365.
- Lord LM, McGinnis C, Densmore C. Addressing the unique needs and quality of life issues for adults receiving long-term home enteral nutrition. Nutr Clin Pract. 2023 Apr 14;38(2):257-76. Available from: https://aspenjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ncp.10965.
- Braga A, Caccia G, Papadia A, Treglia G, Castronovo F, Salvatore S, et al. Urethral bulking agents for the treatment of recurrent stress urinary incontinence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas. 2022 Sep;163:28-37.
- Tunn R, Baeßler K, Knüpfer S, Hampel C. Urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in women. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2023 Feb 3;120(5):71-80. Available from: https://www.aerzteblatt.de/10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0406.
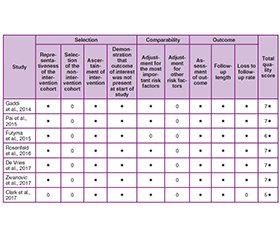
- Gaddi A, Guaderrama N, Bassiouni N, Bebchuk J, Whitcomb EL. Repeat Midurethral Sling Compared With Urethral Bul–king for Recurrent Stress Urinary Incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;123(6):1207-12.
- Pai A, Al-Singary W. Durability, safety and efficacy of polyacrylamide hydrogel (Bulkamid®) in the management of stress and mixed urinary incontinence: three year follow up outcomes. Cent Eur J Urol. 2015;68(4).
- Rosenfeld EC, Christie A, Bacsu CD, Zimmern PE. Macroplastique outcome in women with stress urinary incontinence se–condary to intrinsic sphincteric deficiency. Urol Sci. 2016 Dec;27(4):258-62.
- De Vries AM, van Breda HMK, Fernandes JG, Venema PL, Heesakkers JPFA. Para-Urethral Injections with Urolastic® for Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence: Subjective Improvement and Safety. Urol Int. 2017;99(1):91-7.
- Zivanovic I, Rautenberg O, Lobodasch K, von Bünau G, Walser C, Viereck V. Urethral bulking for recurrent stress urinary incontinence after midurethral sling failure. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017 Mar;36(3):722-6.
- Rodríguez D, Carroll T, Alhalabi F, Carmel M, Zimmern PE. Outcomes of Macroplastique injections for stress urinary incontinence after suburethral sling removal. Neurourol Urodyn. 2020 Mar;39(3):994-1001.
- Serati M, Giammò A, Carone R, Ammirati E, Gubbiotti M, Ruffolo A, et al. Bulking agents for the treatment of recurrent stress urinary incontinence: a suitable option? Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2023 Jan;74(6).
- Futyma K, Miotła P, Gałczyński K, Baranowski W, Doniec J, Wodzisławska A, et al. An Open Multicenter Study of Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Urolastic, an Injectable Implant for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: One-Year Observation. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:1-5.
- Clark R, Welk B. The use of polyacrylamide hydrogel in the setting of failed female stress incontinence surgery. Can Urol Assoc J. 2017 Dec;12(4):95-7.
- Dray EV, Hall M, Covalschi D, Cameron AP. Can Urethral Bulking Agents Salvage Failed Slings? Urology. 2019 Feb;124:78-82.
- Daly CME, Mathew J, Aloyscious J, Hagen S, Tyagi V, Guerrero KL. Urethral bulking agents: a retrospective review of primary versus salvage procedure outcomes. World J Urol. 2021 Jun;39(6):2107-12.
- Long C-Y, Lin K-L, Shen C-R, Ker C-R, Liu Y-Y, Loo Z-X, et al. A pilot study: effectiveness of local injection of autologous platelet-rich plasma in treating women with stress urinary incontinence. Sci Rep. 2021 Jan;11(1):1584.
- Serati M, Braga A, Scancarello C, De Rosa A, Frigerio M, Baruch Y, et al. Does the Polydimethylsiloxane Urethral Injection (Macroplastique®) Improve Sexual Function in Women, in Fertile Age, Affected by Stress Urinary Incontinence? Medicina (B Aires). 2023 Mar;59(3):580.
- Imrey PB. Limitations of Meta-analyses of Studies With High Heterogeneity. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Jan 10;3(1):e1919325. Avai–lable from: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2758468.
- Gandhi AP, Shamim MA, Padhi BK. Steps in undertaking meta-analysis and addressing heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Evid. 2023;1(1):78-92. Available from: https://the.evidencejournals.com/index.php/j/article/view/7.
- Campanella L, Gabrielli G, Chiodo E, Stefanachi V, Pennacchini E, Grilli D, et al. Minimally Invasive Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Prospective Comparative Analysis between Bulking Agent and Single-Incision Sling. Healthcare. 2024 Mar 29;12(7):751. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9032/12/7/751.